Hebei Messi Biology Co., Ltd. stated that hydromagnesite is a natural chemical composition 4MgCO·Mg(OH)·4H2O mineral, and it is an advantageous mineral resource in my country. When hydromagnesite is calcined, magnesium carbonate decomposes, releases carbon dioxide gas and generates magnesia at the same time, the most important factors affecting the activity of magnesia are calcination temperature and time, low activity magnesia is not easy to hydrate, and the reaction activation energy increases. Hexagonal magnesium hydroxide has the advantages of flame retardancy, smoke elimination, safe filling, and low price. It has become an important inorganic flame retardant and has broad market prospects. At present, the production route of hexagonal magnesium hydroxide flame retardant is mainly the sea (halogen) water alkali method and brucite crushing processing, and the hydration of magnesium oxide calcined with hydromagnesite to prepare high-purity hexagonal flakes suitable for high-grade flame-retardant fillers Magnesium hydroxide powder has important industrial value.
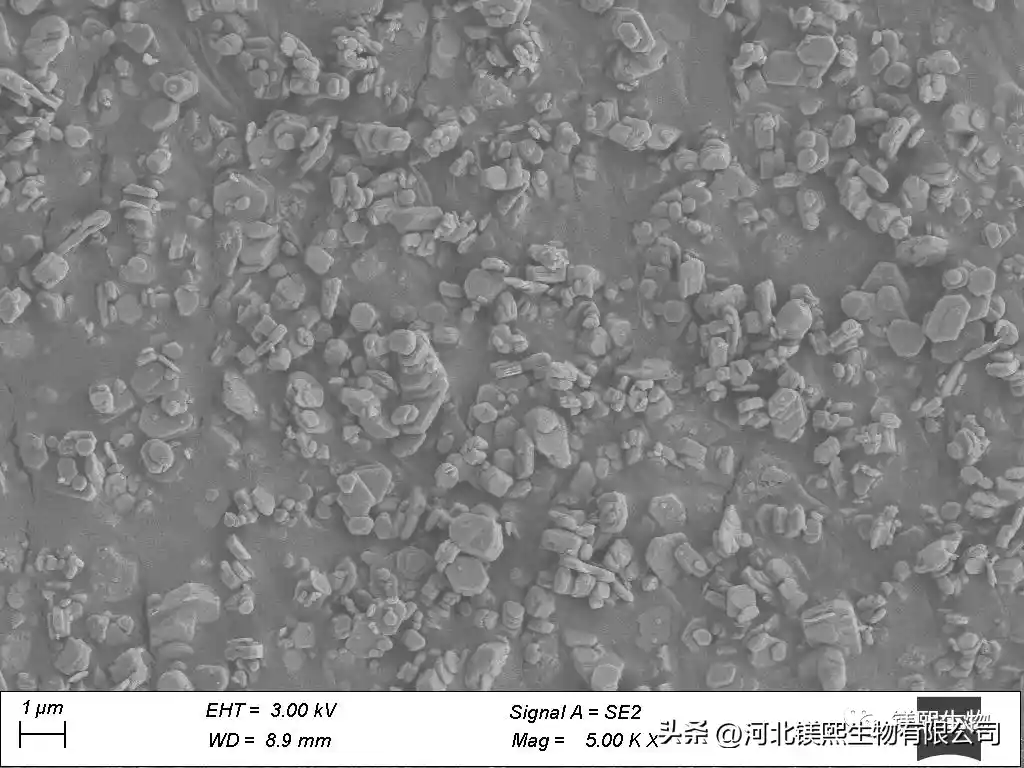
Hebei Messi Biology Co., Ltd. firstly undergoes ball mill crushing, reverse flotation and then positive flotation to purify hydromagnesite. Reverse flotation mainly removes silicate minerals, while forward flotation removes calcium-containing minerals, silicate minerals not exhausted by reverse flotation and other impurities. Positive flotation uses water glass and sodium hexametaphosphate as inhibitors, and oleic acid as collector, which can effectively remove silicon, calcium minerals and other impurities, and the reagents are simple. The content of Si and Ca in the final product magnesium hydroxide obtained by calcining and hydration after flotation decreased significantly, especially the silicate impurities were basically completely removed, and the content of magnesium hydroxide was 99.08%.
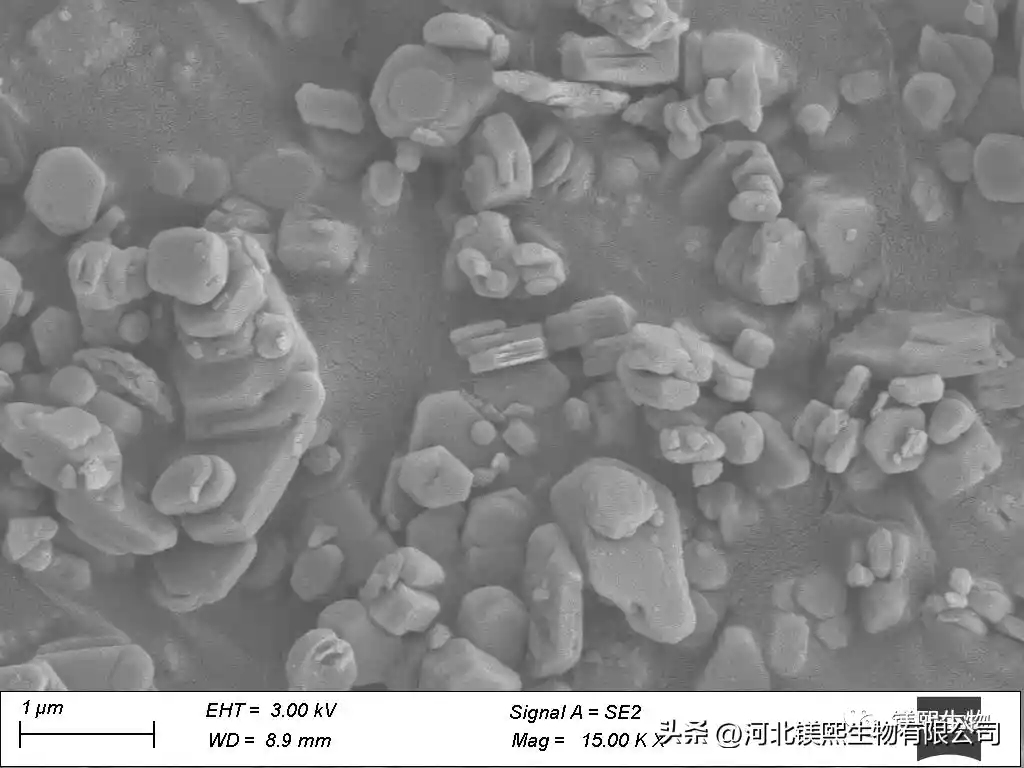
Secondly, the effects of calcination temperature and calcination time on the activity of magnesia were studied. In the case of complete decomposition of hydromagnesite, the activity of magnesium oxide will decrease if the calcination temperature is too high or the time is too long, but if the calcination time is too short, the decomposition of magnesium carbonate may be incomplete. The citric acid method and the hydration method were selected for the determination of the activity of light-calcined magnesium. XRD analysis confirmed that the calcined product was magnesium oxide. The magnesium oxide was used as raw material to carry out hydration reaction to prepare magnesium hydroxide, and the hydration product was confirmed to be magnesium hydroxide by X-ray diffraction. The hydration curves of magnesium oxide at 30°C, 50°C, and 70°C were obtained through experiments, the hydration reaction rate constants at each temperature were calculated, and the hydration activation energy of magnesium oxide was calculated according to the Arrhenius equation. It is 60.7 KJ/mol, which belongs to chemical reaction speed control.
Finally, the effect of hydration reaction conditions on the particle size and morphology of the obtained magnesium hydroxide was investigated. The particle size of magnesium hydroxide was characterized by polarizing microscope combined with Dongtu image processing software, and the microscopic size and shape of the product were observed by scanning electron microscope. The optimal reaction conditions for hydration of magnesium oxide to prepare ultrafine magnesium hydroxide are: 70℃, 2h, concentration of magnesium oxide suspension 0.5mol/L, and adding ethanol is not suitable. The effects of alkali, magnesium salt and dispersant on the particle size and morphology of magnesium hydroxide were studied. Strong alkalinity is not good for the hydration of magnesium oxide to prepare ultrafine magnesium hydroxide.
